Translate this page into:
A boy with type 1 diabetes who could not do ‘Namaste’!

*Corresponding author: Jaivinder Yadav, Department of Pediatrics (Advanced Pediatrics Centre), Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India. jai1984yadav@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Banerjee S, Yadav J, Kumar R. A boy with type 1 diabetes who could not do ‘Namaste’! J Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes. 2023;3:120-1. doi: 10.25259/JPED_2_2024
Abstract
Limited joint mobility (LJM) is a common manifestation of chronic suboptimal glycemic control in type 1 diabetes (T1D). The LJM can be elicited with simple clinical signs. We describe a 13-year-old boy with T1D and LJM.
Keywords
Limited joint mobility
Diabetes
Glycemic control
INTRODUCTION
Limited joint mobility (LJM) is a common manifestation of long-term suboptimal glycemic control in individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D).[1] The syndrome of LJM was described in pediatric literature in 1974 in a series of cases with juvenile diabetes mellitus, short stature, LJM, and sclerodactyly.[1] The LJM can be elicited with simple clinical signs. We describe a 13-year-old boy with T1D and LJM.
CASE DESCRIPTION
A 13-year-old boy (weight-35 kg [−0.9 Z], height 143 cm [−2.41 Z]) with T1D for six years complained of difficulty in finger movements of both hands. He was on a basal-bolus regimen and had suboptimal glycemic control over the years (mean hemoglobin A1c 10.2%, ranging between 9.5% and 11.5%). On examination, the child had contractures and flexion deformity of all interphalangeal joints with wrist joint involvement. The prayer sign and tabletop test were positive [Figure 1]. With all the consistent features and poorly controlled diabetes, the child was diagnosed with LJM. The screening for microvascular and macrovascular complications of T1D was negative.
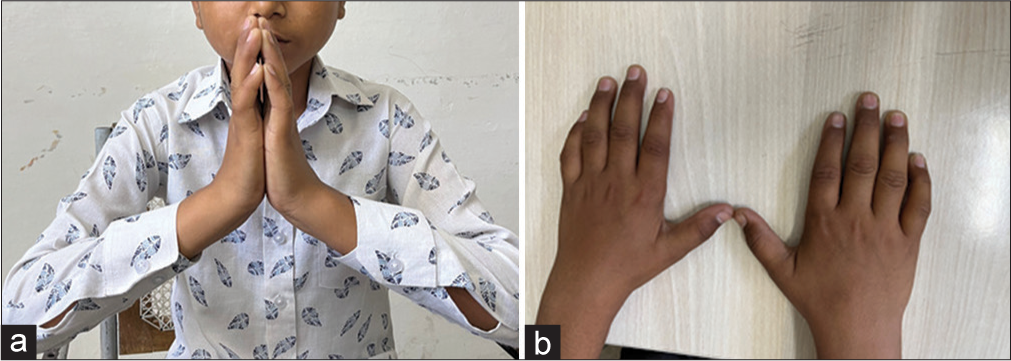
- (a) Prayer Sign - Flexion at metacarpophalangeal, interphalangeal joint, and inability to approximate one or more fingers of both hands by opposition of palmar surfaces of proximal and distal interphalangeal joints with palms pressed together and fingers fanned. (b) Table top sign-Inability to place the fingers or palm flat on the table.
DISCUSSION
The LJM or cheiroarthopathy is a complication of long-term, poorly controlled diabetes. The diagnosis is based on typical painless progressive joint stiffness of hands leading to flexion contractures, but other joints such as wrists, shoulders, and feet may also get involved. The condition occurs as a result of the deposition of advanced glycation products and abnormal cross-linking of increased collagen in joints due to prolonged hyperglycemia.[2]
Tabletop test (putting the palm against a flat surface) and the “Namaste” prayer position are standard clinical methods to detect the condition. However, individual joint examination at the metacarpophalangeal joint, proximal and distal interphalangeal joint, or any other joint for a range of motion and resistance is also recommended.[3,4]
Some studies have shown an association between disease duration, metabolic control, and microvascular complications.[5] The condition is usually irreversible in late stages due to extensive fibrosis and is managed with supportive care and improving glycemic control.[6]
CONCLUSION
We can detect limited joint mobility among children with long-term poor glycemic control using simple signs in clinics.
Ethical approval
The Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript, and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
References
- Contractures in diabetes mellitus: The syndrome of limited joint mobility. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1989;18:168-80.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prayer sign in diabetes mellitus. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2013;17:769-70.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limited joint mobility in type I diabetes mellitus. Indian J Pediatr. 2021;88:415-6.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limited joint mobility syndrome in diabetes mellitus: A mini review. World J Diabetes. 2015;6:1108-12.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limited joint mobility in diabetes mellitus: The clinical implications: The onset is insidious and may predate the recognition of overt disease. J Musculoskelet Med. 2011;28:118.
- [Google Scholar]
- Limited joint mobility in insulin dependent childhood diabetes. Eur J Pediatr. 1990;149:380-8.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






